CEDARS Administrator Manual
CEDARS is provided as-is with no guarantee whatsoever and users agree to be held responsible for compliance with their local government/institutional regulations. All CEDARS installations should be reviewed with institutional information security authorities.
Software Installation
-
Minimum CPU requirements: 16GB Memory and 4 cores [t2.xlarge on AWS]
-
20 GB memory /var directory for storing docker dependencies and data. Might vary depending on your data needs.
-
In order to run, you will need two
.envfiles- The first .env file will be placed under the ROOT DIR
- The second the
.envfile under theCEDARS/cedarsdirectory. - There are
.sample.envfiles available with best default configurations - just RENAME them .env to use defaults.
bash CEDARS/ │ ├── .env ├── docker-compose.yml ├── cedars/ │ ├── .env │ ├── Dockerfile │ └── ...CEDARS/.env: This file contains environment variables used by Docker Compose.CEDARS/cedars/.env: This file contains environment variables specific to cedars application.docker-compose.yml: The Docker Compose configuration file.cedars/Dockerfile: The Dockerfile for building cedars app.
Detailed Requirements
Local Installation Requirement
WARNING
Local installation is not recommended unless you want to modify the underlying codebase. It is recommended to use the Docker deployment method.
For example:
SECRET_KEY=asecurekey
HOST=0.0.0.0
DB_HOST=db
DB_NAME=cedars
DB_PORT=27017
DB_HOST_PORT=27018
DB_USER=admin
DB_PWD=password
DB_PARAMS="authSource=admin"
MINIO_HOST=minio
MINIO_PORT=9000
MINIO_ACCESS_KEY=rootuser
MINIO_SECRET_KEY=rootpassword
ENV=dev
PINES_API_URL=http://pines:8036
REDIS_URL=redis
REDIS_PORT=6379
RQ_DASHBOARD_URL=/rq
PORT=5001
CEDARS is a flask web application and depends on the following software:
-
Python 3.9 - 3.11
You can install Python from the official website.
If you have multiple python versions installed, you can manage the environments using pyenv
Windows Setup Specification
On windows machines for development setups (not using docker) only python 3.9 is supported. If using windows, then installing python via WSL is recommended.
-
Poetry
To install poetry, run pipx install poetry or follow the instructions.
-
Mongo 7.0 or later
For using Mongo, you have multiple options:
- You might use your own enterprise Mongo instance
- You can use a cloud-based service like MongoDB Atlas
- You can run a local instance of Mongo using Docker
- You can run a local instance of Mongo using the official installation
-
Minio
Similar to Mongo, you have multiple options to install MINIO
- You might use your own enterprise MINIO instance
- You can use a cloud-based service like MINIO
- You can run a local instance of MINIO using Docker
- You can run a local instance of MINIO using the official installation
-
Redis
Mac Fork Issue
On MacOS, if you see a issue with fork processes you will need to export OBJC_DISABLE_INITIALIZE_FORK_SAFETY=YES
for running the rq workers
To manage long running processes such as upload, download, spacy labelling, PINES jobs etc.
Docker Requirement
TIP
This is the easiest way to run CEDARS and encapsulates all dependencies above.
TIP
If using docker on windows, it is recommended to install docker via WSL.
Install Docker and Docker Compose.
TIP
Please install docker compose v2 as the spec using deploy which is not compatible with v1.
!!! note "GPU:
`NVIDIA container toolkit` is required for the docker to use GPUs.
Below are the installation steps for CentOS/RHEL. For other OS please refer this nvidia link
# 1. Download the NVIDIA container toolkit repository file
curl -s -L https://nvidia.github.io/libnvidia-container/stable/rpm/nvidia-container-toolkit.repo
# 2. Edit the repository file with the output of (1)
dzdo vi /etc/yum.repos.d/nvidia-container-toolkit.repo
# 3. Install the NVIDIA container toolkit
dzdo dnf install -y nvidia-container-toolkit
# 4. Configure NVIDIA container runtime for Docker
dzdo nvidia-ctk runtime configure --runtime=docker
# 5. Restart the Docker service to apply changes
dzdo systemctl restart docker
System Architecture
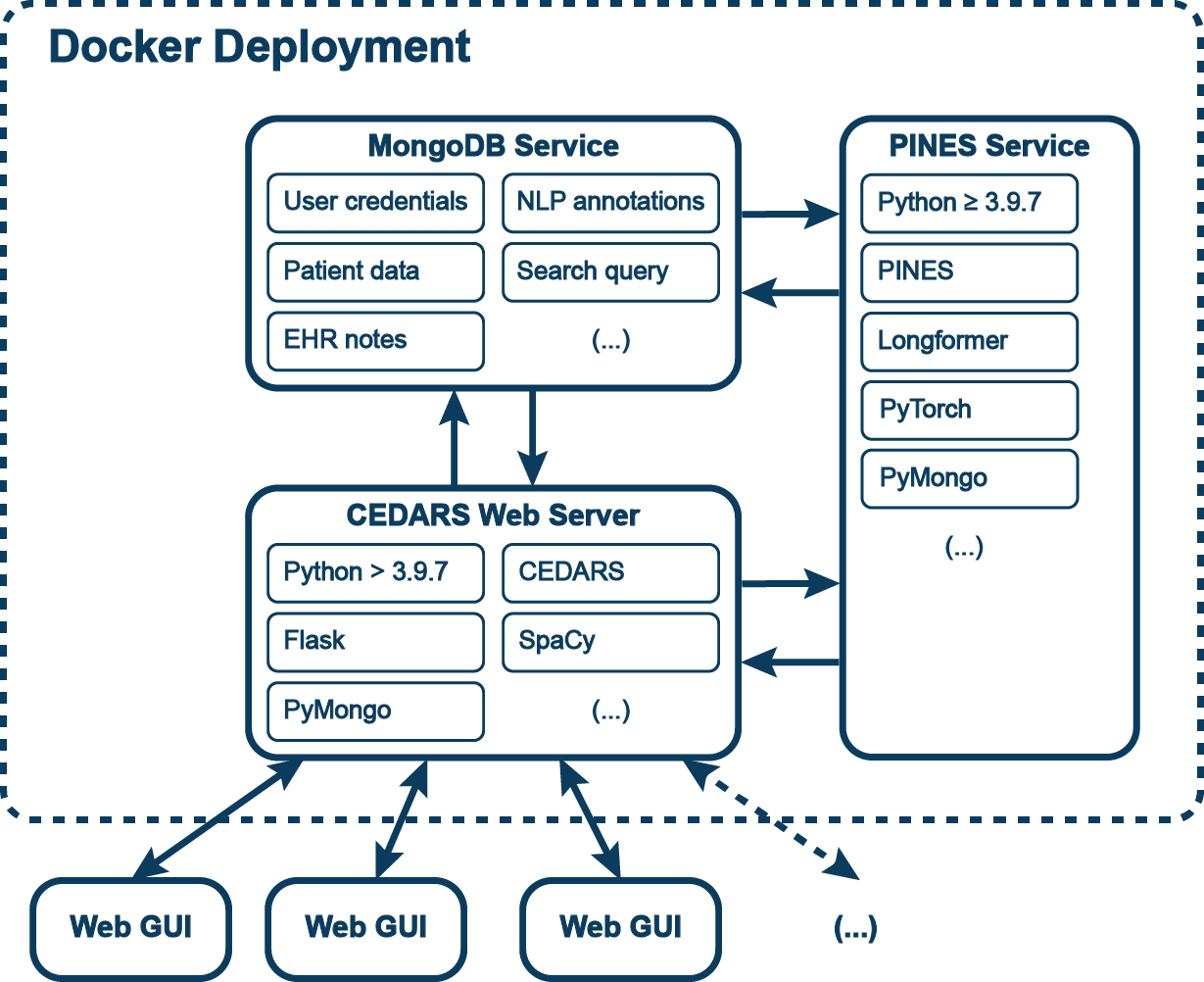
The CEDARS application runs on a web server and generates an online graphical user interface (GUI) using Flask. All data are stored in a MongoDB instance hosted separately. However, most CEDARS instances are dockerized in order to streamline the project setup process and ensure adequate compatibility of dependencies.
Once the instance is running, electronic health record (EHR) documents are imported and processed through the CEDARS natural language processing (NLP) pipeline. Additional document annotation with a PINES model is optional. A CEDARS annotation project can be set up entirely from the GUI, using the administrator panel. The existing annotations can be downloaded at any point from this interface.
Annotators can connect to the CEDARS app by accessing a web URL provided by the administrator. CEDARS performs the operations to pull selected documents from the database, process them and present them to the annotators. Data entered by users is processed by CEDARS and saved to the database. Multiple users can work on one CEDARS project at the same time. The application will automatically select individual patient records for each user. Record locking is implemented to prevent collisions and inconsistencies.
Installing CEDARS
To install CEDARS, please start by cloning the repository and installing the required dependencies. You can then run the app locally or using Docker.
- Clone the Repo:
git clone git@github.com:CEDARS-NLP/CEDARS.git - Change directory:
cd CEDARS - Initialize submodules:
git submodule init - Download submodules:
git submodule update
git submodule update time out
If you are accessing git over http - take following steps
- update .gitmodules in the root dir with
url = https://github.com/CEDARS-NLP/PINES.git
- Run: git submodule sync
- Run: git submodule update
Standalone CEDARS Python Package Installation
Make sure all the local requirements above are met. Then, you can install the package using Poetry:
$ cd cedars
$ poetry install # do not cd into cedars/app
$ poetry run python -m app.wsgi
Setting Up VS Code Debugger for Flask Application (OPTIONAL)
If you are a developer and wish to use a code debugger while working with CEDARS, then you can follow the steps below to setup a VS Code debugger.
1. Create a python virtual environment (preferably using [pyenv](https://github.com/pyenv/pyenv?tab=readme-ov-file#installation)).
2. Create a profile in launch.json (VS Code) as defined in [this](https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/python/tutorial-flask#_run-the-app-in-the-debugger) article.
3. Set FLASK_APP variable to “app/wsgi.py” in the new launch.json you created.
4. Follow these [instructions](https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/python/environments) to load the python virtual environment you created in step 1. into VS Code.
5. Select you new debugger profile in the debugger tab and run it.
Docker Deployment
The most straightforward way to complete a CEDARS project is via docker containers. This approach allows fast and reliable installation on prems or in the cloud with on-demand access to compute resources, including graphics processing unit (GPU). Inclusion of required dependencies in the containers mitigate the problems associated with version incompatibilities inherent to ad hoc builds. Docker images can be easily installed in air-gapped environment, which is sometimes an institutional requirement. A CEDARS docker deployment will include:
- CEDARS Flask web server
- MongoDB database service
- MINIO object storage service
- PINES NLP annotation service (optional)
Each component runs as a service encapsulated in a docker container. Those three elements a coordinated within a deployment.The PINES service requires a GPU for model training. This is optional for inference (i.e. annotating documents).
After cloning as described above, create required .env files as mentioned here
After creating .env files, run the following commands:
$ cd CEDARS
# if you do are not using GPU and want all the services to be hosted on docker
$ docker compose --profile cpu --profile selfhosted up --build -d
# if you are using a GPU
$ docker compose --profile gpu --profile selfhosted up --build -d
# if you want to use a native service such as AWS Document DB
$ docker compose --profile gpu up --build -d # gpu
$ docker compose --profile cpu up --build -d # cpu
Once all services are started - the app will be available here
http://<hostaddress>:80
AWS/Server Deployment
- Install docker: Ubuntu
-
Make sure you have docker compose v2 if you are running docker as sudo - please follow this stackoverflow link to run as a non-sudo
-
Install compose v2 using this link
For example to use AWS DocumentDB with tls you can create .env (under CEDARS/cedars) file like this
DB_HOST=<your-cluster-ip>.docdb.amazonaws.com
DB_NAME=cedars
DB_PORT=27017
DB_USER=<docdbuser>
DB_PWD=<docDBpassword>
DB_PARAMS="tls=true&tlsCAFile=global-bundle.pem&replicaSet=rs0&readPreference=secondaryPreferred&retryWrites=false"
Project Execution
Overview
Determining clinical event dates with CEDARS is a simple, sequential process:

After generation of a CEDARS instance, EHR documents are uploaded, a keyword search query is generated and automatic NLP annotations are launched, following which manual data entry can begin. If known event dates exist, those can be imported before annotator work starts. Once all patient records have been annotated manually for clinical events, the dataset can be downloaded and used immediately in time-to-event analyses. Alternatively, estimated event dates can be obtained without the human review step if a PINES model of satisfactory accuracy was used to classify documents.
The package authors suggest that a random sample of patients be selected for manual review via independent means. If performance metrics are unsatisfactory, the search query can be modified and CEDARS annotations updated through the same process.
Setting Up a CEDARS Project and Users
The first step after running CEDARS is to set up a new project. This is done by the administrator through the GUI. The following steps are required:
1. At first login, the administrator will be prompted to register a new user. This user will be the administrator of the project.
2. The administrator will then fill in Project Details such as Project Name.
3. The administrator can also create new users who will only work on the Annotation Interface.
4. Administrator will provide the credentials to the annotators.
Electronic Health Record Corpus Upload
Keyword Search Query Design
The CEDARS search query incorporates the following wildcards:
"?": for one character, for example "r?d" would match "red" or "rod" but not "reed"
"*": for zero to any number of characters, for example "r*" would match "red", "rod", "reed", "rd", etc.
CEDARS also applies the following Boolean operators:
"AND": both conditions present "OR": either present present "!": negation, for example "!red" would only match sentences without the word "red"
Lastly, the "(" and ")" operators can be used to further develop logic within a query.
Search Query Implementation
Expected query will be a set of keywords separated by OR keyword.
Each expression separated by OR can have expressions combined by AND or NOT and the keywords can also contain wildcards.
Spacy Requirements:
- ! - negation
- Each dictionary in a list matches one token only
- A list matches all the dictionaries inside it (and condition)
- A list of list contains OR conditions
- [{"TEXT": {"REGEX": "abc*"}}] represents one token with regex match
- [{"LOWER": "dvt"}] matches case-insenstitive DVT
- [{"LEMMA": "embolus"}] matches the lemmatized version of embolus as well in text
Implementation:
- Split the query by OR
- Split each expression by AND
- Split each expression by NOT
- Split each expression by wildcard
- Convert each expression to a spacy pattern
- Combine the patterns
- Return the combined pattern
Source code in cedars/app/nlpprocessor.py
29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 | |
Natural Language Processing Annotations
The process of automatically parsing clinical documents before presentation to an annotator is performed in three steps:
1. NLP annotation via the SpaCy traditional NLP pipeline: In this step, sentence boundaries, lemmas and negation status are characterized.
Negation Detection
This function takes a spacy token and determines if it has been negated in the sentence.
Ex.
This is not an apple.
In the above sentence, the token apple is negated.
| Parameters: |
|
|---|
| Returns: |
|
|---|
Source code in cedars/app/nlpprocessor.py
78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 | |
2. Keyword query matching: only documents with at least one sentence matching the search query are retained. Sentences from documents without a matched will be marked as reviewed. Patients with no remaining sentences/documents will be considered not to have sustained the event of interest and will not be reviewed manually.
Process Query Matching
This function takes a medical note and a regex query as input and annotates the relevant sections of the text.
Source code in cedars/app/nlpprocessor.py
145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 | |
3. Transformer model labelling (optional): individual documents are labelled for their probability (p) of occurring at or after a clinical event. This last step is facultative and offers the possibility of further narrowing the scope of material to be reviewed manually, further improving efficiency. Documents with a p inferior to the predetermined threshold and their associated sentences are marked as reviewed. Patients with no remaining sentences/documents will be considered not to have sustained the event of interest and will not be reviewed manually.
PINES predictions
Get prediction from endpoint. Text goes in the POST request.
Source code in cedars/app/db.py
1666 1667 1668 1669 1670 1671 1672 1673 1674 1675 1676 1677 1678 1679 1680 1681 1682 1683 1684 1685 1686 1687 1688 1689 1690 1691 1692 1693 | |
Save PINES predictions
Predict and save the predictions for the given text_ids.
Source code in cedars/app/db.py
1788 1789 1790 1791 1792 1793 1794 1795 1796 1797 1798 1799 1800 1801 1802 1803 1804 1805 1806 1807 1808 1809 1810 1811 1812 1813 1814 1815 1816 1817 1818 1819 | |
Event Pre-Loading
Sometimes a cohort of patients will already have been assessed with other methods and CEDARS is used as a redundant method to pick up any previously missed events. In this use case, a list of known clinical events with their dates will exist. This information can be loaded on CEDARS as a "starting point", so as to avoid re-discovering already documented events.
Manual Assessment for Clinical Events
The process by which human abstractors annotate patient records for events is described in the End User Manual. This step can be skipped altogether if a PINES model was used to classify documents. An estimated event date will be generated by PINES. Transformer models often exhibit sufficient performance to be used without individual record review, but an audit step as detailed below is strongly advised to confirm satisfactory sensitivity, specifcity and event time estimation.
Error Handling and Queues
All the jobs are processed at a patient level. For each patient, a job is submitted to a rq. If a job fails, it is retried 3 times before moving it a failed queue.
Queue Operations
docker ps- to see list of all docker containsdocker exec -it <any-worker-docker-container-id> bashexport REDIS_HOST=redis- the service name in nginx/nginx.confrq info(status)rq requeue --queue cedars -a(requeue all failed jobs)
Launch a task and add it to Mongo if it doesn't already exist.
TODO: insert only one
Source code in cedars/app/db.py
1822 1823 1824 1825 1826 1827 1828 | |
Dataset Download
Once there are no patient records left to review, event data can be downloaded from the database via the GUI Detailed information is provided including clinical event dates, individual annotator contribution and review times. If a PINES model was used but no manual annotations were applied, estimated event dates can be used in a time-to-event analysis instead of manual entry.
Download Completed Annotations
This generates a CSV file with the following specifications: 1. Find all patients in the PATIENTS database, these patients become a single row in the CSV file. 2. For each patient - a. list the number of total notes in the database b. list the number of reviewed notes c. list the number of total sentences from annotations d. list the number of reviewed sentences e. list all sentences as a list of strings f. add event date from the annotations for each patient g. add the first and last note date for each patient 3. Convert all columns to proper datatypes
Source code in cedars/app/ops.py
854 855 856 857 858 859 860 861 862 863 864 865 866 867 868 869 870 871 872 873 874 875 876 877 878 879 880 881 882 | |
Audit
CEDARS is by definition semi-automated, and depending on the specific use case and search query some events might be missed. This problem should be quantified by means of a systematic, old-fashion review of randomly selected patients. Typically, at least 200 patients would be selected and their corpora reviewed manually for events. Alternatively, a different method (e.g. billing codes) could be used. This audit dataset should be overlapped with the CEDARS event table to estimate sensitivity of the search query in the cohort at large. If this parameter falls below the previously established minimum acceptable value, the search query scope should be broadened, followed by a database reset, uploading of previously identified events and a new human annotation pass, followed by a repeat audit.
Project Termination
Once all events have been tallied and the audit results are satisfactory, if desired the CEDARS project database can be deleted from the MongoDB database. This is an irreversible operation.
In future, there will be way to archive CEDARS projects, but this feature is not yet available.
Issues
- Unable to install
thinc- downgrade python version < 3.12
Terminate the Project
Reset the database to the initial state.
Source code in cedars/app/db.py
2033 2034 2035 2036 2037 2038 2039 2040 2041 2042 2043 2044 2045 2046 2047 2048 2049 2050 2051 2052 2053 2054 2055 | |